Varicocele Treatment in Aurangabad
Varicocele Embolization Treatment in Aurangabad
Varicoceles generally structure during adolescence and foster over the long run. They might cause distress or agony, yet they frequently bring about no side effects or confusion.
A varicocele might cause an unfortunate improvement of a gonad, low sperm creation, or different issues that might prompt barrenness. Medical procedures to treat varicocele might be prescribed to address these confusions.
Symptoms
A varicocele usually occurs on the left side of the scrotum and often produces no signs or symptoms. Possible signs and symptoms may include:
- Pain. A dull, aching pain or discomfort is more likely when standing or late in the day. Lying down often relieves pain.
- A mass in the scrotum. If a varicocele is large enough, a mass like a “bag of worms” may be visible above the testicle. A smaller varicocele may be too small to see but noticeable by touch.
- Differently sized testicles. The affected testicle may be noticeably smaller than the other testicle.
- Infertility. A varicocele may lead to difficulty fathering a child, but not all varicoceles cause infertility.
- Visible lump or swelling in the scrotum
- Dull and recurring pain in the scrotum
- Swelling and intensifying pain around the scrotum
- Visibly twisted veins in the scrotum
- Feeling of heaviness in the testicles
How common are varicoceles?
- Varicocele’s are very common, and they are not dangerous.
- In fact, 15% of all adult men have a varicocele.
- For many men, their varicocele will go unnoticed throughout their life, or it will not cause any problems at all.
- . About 20% of adolescents have varicoceles, so a fraction of them likely resolve spontaneously.
When are varicoceles usually found?
- Most commonly, its found in a completely asymptomatic man being evaluated for infertility.
- A mass in the scrotum may be detected by the patient or by a physician during routine exam.
- A man may present to a physician with pain in the scrotum.
Why might I need varicocele embolization?
- Varicoceles usually don’t have any symptoms. In teens, they may cause slowed growth of the testicles. They may also cause pain and swelling.
- You may get treatment due to your symptoms or because of infertility.
- Surgery and varicocele embolization are the 2 main treatments. Both choices have similar success rates. But the recovery time from embolization is usually shorter.
- Surgery might be a better choice if you have varicocele affecting both testicles.
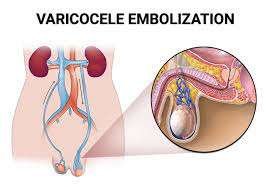
What are the risks of varicocele embolization?
- Infection
- Allergic reaction
- Excess bleeding
- Migration of the coil sometimes used to block the enlarged vein
- Lower back pain
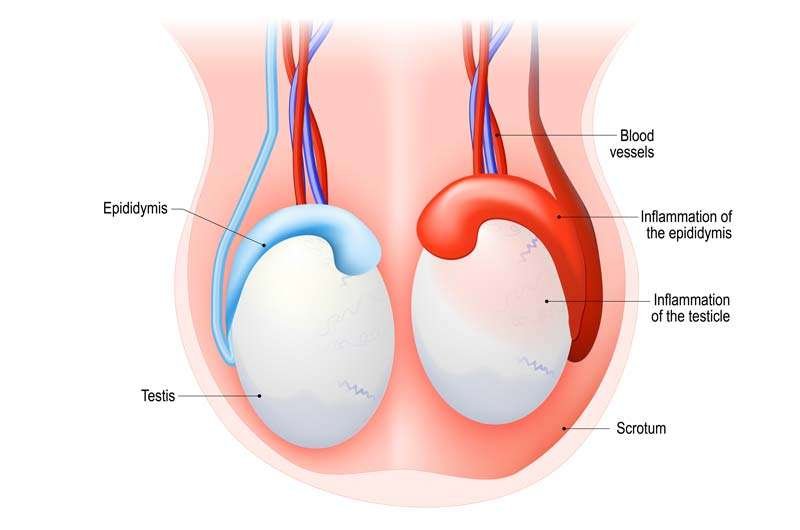
- Inflammation of the scrotum
- Inflammation of the vein
- Nausea
FAQ's
Frequently Asked Question
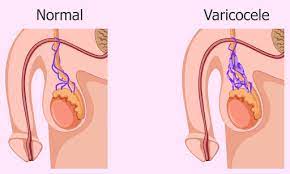
A varicocele is a network of tangled blood vessels in the scrotum. Varicocele usually develops slowly. They are more common in men aged 15-25 years and are most often seen on the left side of the scrotum. It is a leading cause of male infertility and may also cause pain and shrinkage of the testicles. Fortunately, most varicoceles are easy to diagnose and, if they cause symptoms, can be repaired surgically.
Varicocele occurs in the scrotum. It is similar to the varicose veins that occur in the leg. They are most commonly found on the left side of your scrotum. Varicoceles can exist on both sides but are extremely rare.
Yes, varicocele is common. It can be found in 15 percent of the adult male population and 20 percent of adolescent males. They are common in males aged between 15 to 25.
A varicocele is diagnosed after a physical exam. If the results are inconclusive, your doctor may need to perform a scrotal ultrasound.